Remapping Accessors
In the previous section we learned how the Velociraptor’s path
handling allows for precise and correct path manipulations. The OSPath
abstraction allows VQL plugins and functions to open files in a
consistent way using different accessors. For example we have seen how
files can be read inside a zip file easily, while still using the
familiar glob() plugin.
For example the following query applies the yara() plugin to search
inside a zip file:
SELECT * FROM foreach(row={
SELECT OSPath
FROM glob(
globs="**",
root=pathspec(DelegatePath="F:/hello.zip"),
accessor="zip")
}, query={
SELECT * FROM yara(rules=YaraRules, accessor="zip", filename=OSPath)
})
Where the glob() plugin searches for files within the zip file
hello.zip and passes the OSPath into the yara() plugin.
One downside to this query is that an initial OSPath object needed
to be built to access the zip file itself. This means that we can not
generally use existing VQL artifacts or queries and just apply them in
a zip file, because they need to build the initial OSPath objects
themselves.
For example, the following query uses yara() to search files on the
filesystem:
SELECT * FROM foreach(row={
SELECT OSPath
FROM glob(globs="**", root="C:/", accessor="auto")
}, query={
SELECT * FROM yara(rules=YaraRules, accessor="auto", filename=OSPath)
})
If we created an artifact with this query in it, then how can we use the same existing artifact within a zip file instead of on the filesystem?
Comparing the two queries above we can see they are very similar. The only thing that is really different between them is the path and the accessor used, the general VQL query is exactly the same.
Remapping and VQL
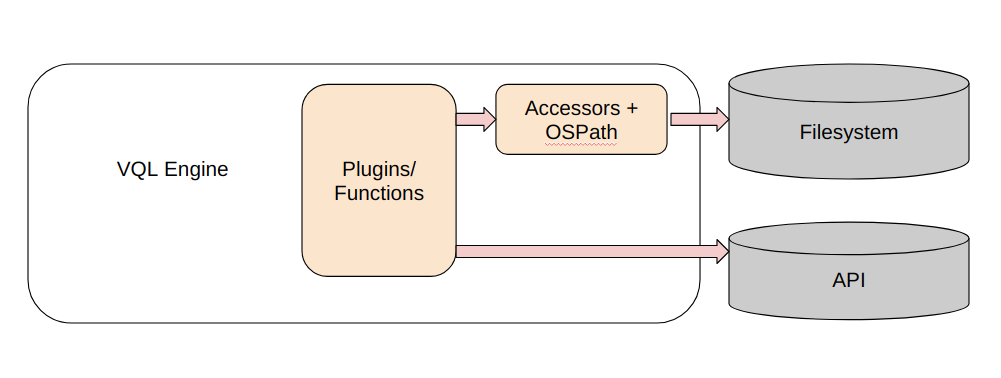
Velociraptor’s VQL engine is a powerful and efficient language interpreter which allows running powerful queries. You can think of the VQL engine as a sandbox interpreting the VQL queries. However, there are really only two ways for VQL queries to interact with the system:
- Using accessors and OSPath objects allows VQL queries to access various filesystem like constructs (e.g. registry, zip files etc).
- Using specific plugins and VQL functions allows queries to call APIs on the host.
The idea behind remapping rules is to provide a system for mapping
certain accessors into other accessor names so as to turn the generic
query above from using the auto accessor into automatically using the
zip accessor. This allows us to virtualize the VQL query to run in
a different context - for example a query designed to run on the live
filesystem can simply run on a dead disk image.
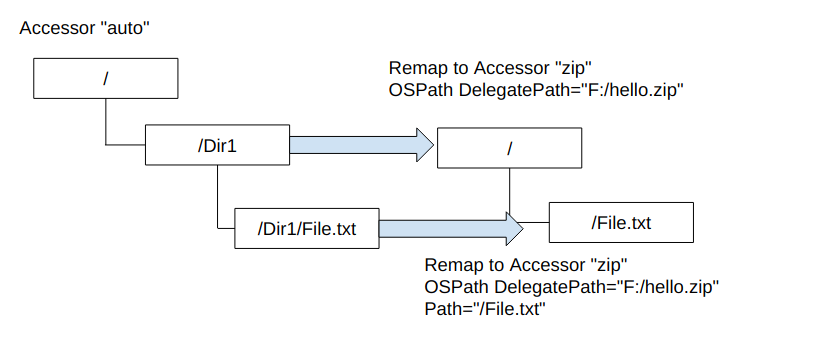
Consider the remapping configuration illustrated above. In this
configuration, when a plugin uses the “auto” accessor with a path like
“/Dir1”, the “zip” accessor is used instead with an OSPath of
{DelegatePath="F:/hello.zip"}. This happens transparently once the
mapping rule is set up!
In the notebook, remapping rules are installed using the remap()
plugin and apply to all queries following the remap rule.
Let’s configure a small remapping rule example in a notebook:
LET _ <= remap(config='''
remappings:
- type: mount
from:
accessor: zip
prefix: |
{
"DelegateAccessor": "auto",
"DelegatePath": "F:/hello.zip",
"Path": "/"
}
on:
accessor: "auto"
prefix: "/"
path_type: "windows"
''')
SELECT OSPath FROM glob(globs="*", accessor="auto", root="/")
This rule defines a remapping on the auto accessor at the root
level. The auto accessor will treat paths as windows path type. When
a plugin attempts to open a file using the auto accessor, the
remapping engine will instead use the zip accessor, and create an
OSPath that is constructed by adding the auto path into the zip
path. So opening a file called hello.txt with the auto accessor
will actually produce
accessor: zip
path: {
"DelegateAccessor": "auto",
"DelegatePath": "F:/hello.zip",
"Path": "/hello.txt"
}
Dead disk analysis
This remapping is useful to virtualize a query and allow it to run in a different environment than it was initially designed for. This allows us to reuse artifacts in different contexts. For example, a live artifact can be reused with a dead disk image.
Click this link to learn more about how to create remapping files for dead disk analysis